Notes: How the Legislative Branch is Set UP
What is a Census? What is Reapportionment?
A census is taken every ten years. This is a population count that determines how many representatives a state will receive in the House of Representatives.
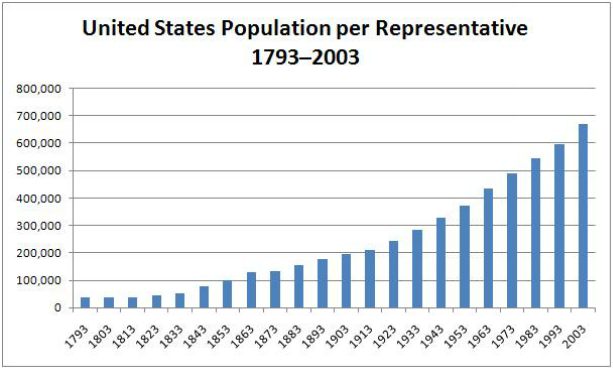
The ratio of representatives per person has grown since the formation of the United States. In 1789, there were less than 30,000 people per representative. In 2003, there was one representative for every 675,000 people.
This is not only important in the House of Representatives, but in the Electoral College as well. Electoral College votes are based on the state's total number of Senators (2) plus the number of House of Representative members, which is based on population.
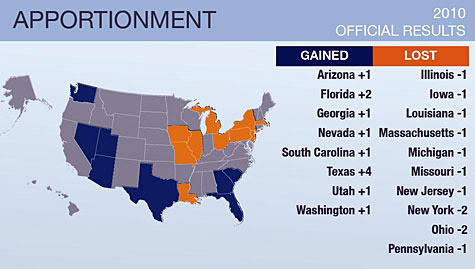
After a census is taken, reapportionment will occur. This is the re-distribution of representatives, based on changes in a state's population. States that significantly increase their population will be given more representatives. States that decrease in population will lose representatives. California, for example, currently has 53 members in the House of Representatives. In 1940, they had 20. As their population has increased, they've been reapportioned every ten years with more representatives. The chart below shows how apportionment changed during the 2010 census. Notice which states lost the most; and gained the most. The next census will take place in 2020.
The ratio of representatives per person has grown since the formation of the United States. In 1789, there were less than 30,000 people per representative. In 2003, there was one representative for every 675,000 people.
This is not only important in the House of Representatives, but in the Electoral College as well. Electoral College votes are based on the state's total number of Senators (2) plus the number of House of Representative members, which is based on population.
After a census is taken, reapportionment will occur. This is the re-distribution of representatives, based on changes in a state's population. States that significantly increase their population will be given more representatives. States that decrease in population will lose representatives. California, for example, currently has 53 members in the House of Representatives. In 1940, they had 20. As their population has increased, they've been reapportioned every ten years with more representatives. The chart below shows how apportionment changed during the 2010 census. Notice which states lost the most; and gained the most. The next census will take place in 2020.
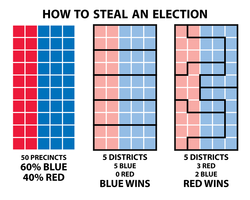
What is Gerrymandering?
What is a Filibuster? / Reapportionment
|
|
|
Polls; Congress; Incumbents / Pork Barrel Spending
|
|
|